financial risk management course
 |
| How to Master Risk Management: A Complete Guide |
Welcome to the blog post we have today where we explore the intriguing field of risk management. Understanding and putting into practise good risk management techniques has become essential for both firms and individuals as markets continue to change and uncertainty becomes a regular companion. This essay will go through the fundamentals of risk management, the significance of it, and useful strategies for navigating the volatile market.
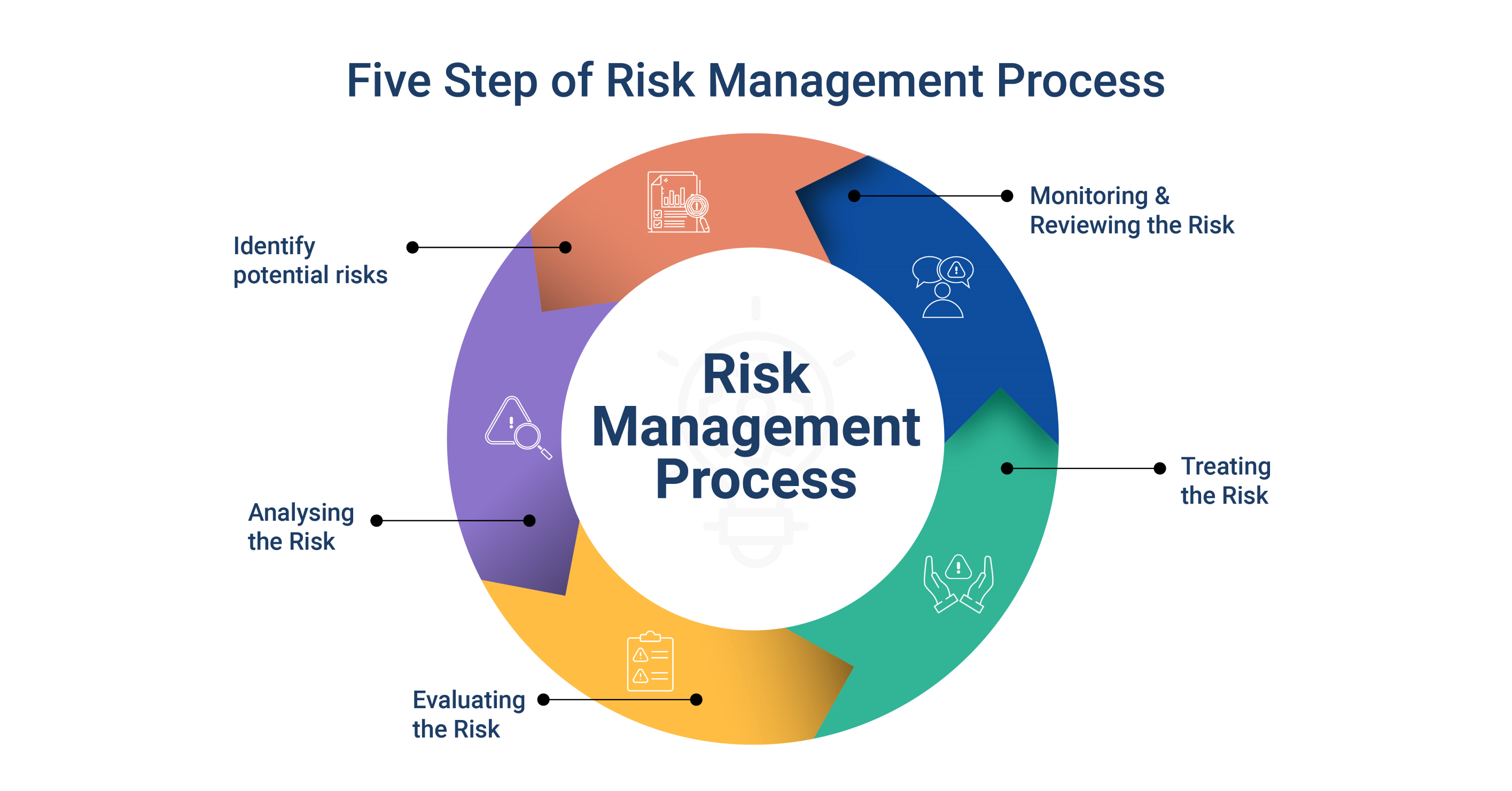
1. What is Risk Management?
 |
| what is Risk |
The process of recognising, evaluating, and prioritising risks in order to reduce potential losses or bad effects while maximising opportunities is known as risk management. It entails creating plans to reduce risks, making wise choices, and keeping a good balance between reward and risk.
2. Why Risk Management Is Important:
 |
| Importance of Risk Management |
a. Preserving Capital: By reducing the likelihood of catastrophic losses, effective risk management protects your financial resources. You can safeguard your investments and guarantee long-term sustainability by recognising and reducing potential risks.
b. Making decisions: Risk management offers a structured method for making decisions. You can use it to assess risks objectively, take into account possible results, and make decisions based on a complete knowledge of the risks involved.
c. Competitive Advantage: By being proactive rather than reactive, organisations that prioritise risk management obtain a competitive edge. They are able to recognise new dangers, grasp chances, and quickly adjust to shifting market conditions.
3. Important Elements of Risk Management:
 |
| Elements of Risk management |
a. Risk Identification: Finding possible risks is the first stage in risk management. This entails mapping out potential weaknesses and analysing internal and external elements that could have an impact on your goals.
b. Risk Assessment: After risks are discovered, they must be evaluated for their likelihood and potential consequences. This enables you to properly prioritise risks and manage resources.
c. Risk Mitigation: Developing ways to reduce risks comes after identifying the risks. This could entail putting controls in place, transferring risk via insurance, diversifying your finances, or making backup plans.
d. Review and Monitoring: Risk management is a continuous process. You can adjust to changing circumstances, spot new hazards, and reevaluate old ones through regular monitoring and review.
4. Risk-management methods include:
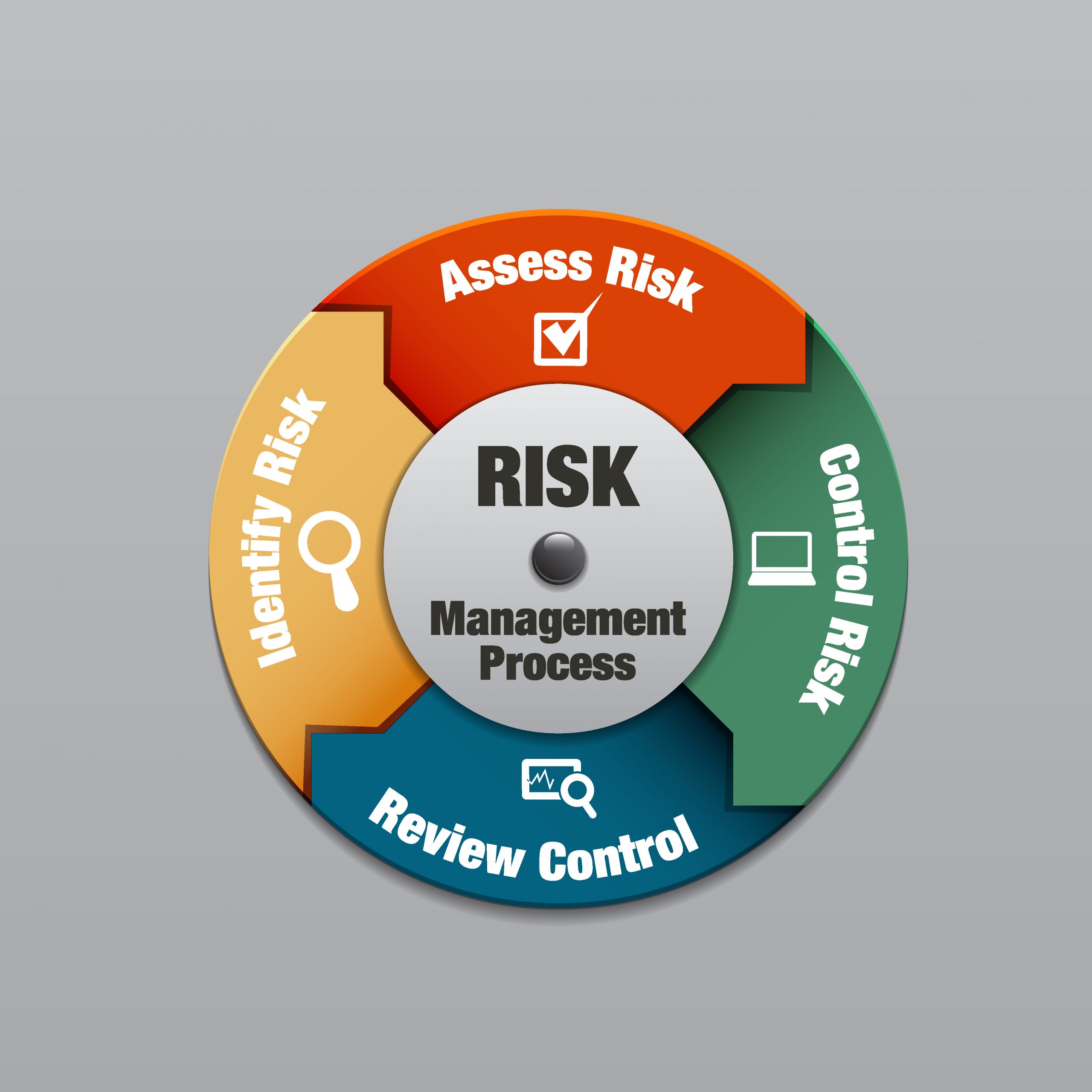 |
| 4 Methods to manage Risk |
a. Diversification: By spreading assets across various asset classes or industries, you can lessen the impact of individual risks and create a portfolio that is more evenly distributed.
b. Hedging: Hedging entails the use of financial tools or techniques to counteract prospective losses. Derivatives, for instance, can be used to protect against price changes.
c. Insurance: Transferring risk via insurance contracts can shield you from unanticipated occurrences like property damage or liability lawsuits.
d. Scenario analysis: Scenario analysis helps identify possible hazards and create effective risk response strategies by modelling various situations and evaluating their impact.
5. The management of risk and emotional restraint:
 |
| Managing the Risk |
Emotional control is a risk management strategy that is frequently disregarded. Emotions have the potential to impair reason and cause irrational behaviour. By exercising emotional restraint, you can stick to your risk-management strategy and prevent taking rash decisions motivated by greed or fear.
Conclusion:
Successful investing and commercial operations depend critically on effective risk management. You may confidently navigate the market's uncertainty by comprehending the guiding concepts and putting them into practise. Keep in mind that risk cannot be completely removed, but it may be handled effectively. To ensure a bright future, be proactive, adjust to shifting conditions, and give risk management first priority.
Disclaimer: This article only offers general information and is not intended to be a source of expert business or financial advice. Before making any decisions about investments or risk management, always seek the advice of a certified professional.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Ques: What are the 4 principles of risk management?
Ans: A strong risk management culture inside an organisation is characterised by five major principles: (1) the competence to make decisions in advance; (2) sufficient resources and capacity to adjust to shifting circumstances; (3) unrestricted information flow into and throughout the organisation; and (4) a readiness to learn and adapt.
Ques: What are the 4 C's of risk management?
Ans: The systematic examination of credit risk is aided by the four credit criteria. They offer a structure within which data could be acquired, divided, and examined. It organises the data into four major categories: character, capacity, capital, and conditions.
Ques: What are the 4 types of risk?
Ans: The main four types of risk are:
strategic risk:- strategic risk, such as a new competitor entering the market.
compliance and regulatory risk:- Risk related to compliance and regulations, such as the introduction of new laws or regulations.
financial risk:- Financial risk, such as an increase in interest rates on your business loan or a customer who doesn't pay.
operational risk:- operational risk, such as the failure or theft of important machinery.
Ques:What are the basics of risk?
Ans: Generally, ambiguity leads to risk.
This risk can arise in organisations from a variety of sources, including project failure, accidents, natural disasters, and market uncertainty (demand, supply, and stock market). Depending on the type of risk, there are several tools to handle the same.
Comments
Post a Comment